Are you among the many IT departments that struggle to demonstrate clear business value, often operating as reactive cost centers rather than strategic enablers? In that case, Understanding “What is ITIL?” and how the ITIL framework changes this dynamic by providing proven methodologies is crucial for changing this situation.
5 Must-Adapt IT Operations Trend Before 2030
This ebook provides a clear, executive-level perspective on 5 forces redefining IT operations in the next 5 years. The strategic decisions leaders must act now to stay ahead.
Download for Free
To help you with that, this guide explains the fundamentals, the latest version 4 model, and why enterprise leaders across Asia-Pacific are using this framework to transform IT operations.

What is ITIL in simple terms? And The Evolution to ITIL 4
ITIL stands for Information Technology Infrastructure Library. It is a globally recognized framework that helps organizations align their IT services with business objectives and deliver measurable value.
Think of this as a comprehensive playbook containing proven best practices for managing the entire IT service lifecycle, from initial planning through ongoing improvement.
ITIL transforms IT departments from reactive support teams into strategic business partners that drive measurable results.
What is the main goal of ITIL and its origin?
In the early 1980s, the British government faced a critical problem: IT departments operated in chaos. Each agency invented its own processes, leading to unpredictable service quality, budget overruns, and knowledge trapped in individuals’ heads. When staff left, their expertise vanished. Leadership couldn’t measure IT performance or justify spending.
The Central Computer and Telecommunications Agency (CCTA) responded by documenting proven IT service management practices into over 30 volumes—the original Information Technology Infrastructure Library (ITIL).
Its core goal: Transform IT from an unpredictable cost center into a measurable service function that consistently delivers business value through standardized, repeatable processes.
Private organizations quickly recognized these same pain points and adopted it globally. Key milestones accelerated this:
- 2001: Integration with the Office of Government Commerce expanded international reach
- 2005: ITIL formalization into the ISO/IEC 20000 standard
- 2013: Transfer to AXELOS enabled commercial innovation
- 2019: ITIL 4 adapted the framework for cloud, DevOps, and agile environments
Despite four decades of evolution, the purpose remains: enable IT operations that are predictable, measurable, and continuously improving in alignment with business needs.
ITIL v4: The Latest Approach
The framework recognizes that modern IT environments – characterized by cloud adoption, DevOps practices, and agile development – require iterative improvement rather than wholesale transformations.
While keeping proven practices like Incident and Change Management, it replaces rigid processes with flexible approaches that work alongside DevOps, Agile, and cloud technologies.
The old 5-stage lifecycle is now the Service Value System – a more flexible model focused on delivering value, not just following procedures. ITIL v4 treats IT service management as a partnership between IT and business, emphasizing quick iterations over massive transformations.
The cornerstone of understanding ITIL v4 lies in its Four Dimensions of Service Management:
- Organizations and People – skills, culture, teams
- Information and Technology – tools and data
- Partners and Suppliers – vendor relationships
- Value Streams and Processes – workflows that deliver results
This approach ensures technology decisions consider human factors, vendor relationships, and business workflows simultaneously. It creates more resilient, adaptable IT operations that actually support business goals.
AI Integration with ITIL 4
AI technology significantly enhances ITIL 4 service management practices by automating routine tasks and reducing human error. Current AI applications in ITSM include:
- Predictive Analytics: Identifying and resolving potential incidents before they escalate
- Service Desk Automation: Categorizing, assigning, and resolving tickets automatically
- Continuous Monitoring: Real-time threat detection and system surveillance
- User Support: Chatbots providing immediate assistance for common issues
- Personalization: Analyzing user data to create tailored service offerings
- Performance Analysis: Identifying improvement opportunities through data insights
This AI integration supports ITIL 4’s emphasis on flexibility and continuous improvement, helping organizations build more efficient and responsive IT service management capabilities.
What are the 5 stages of ITIL?
The following five interconnected stages span the complete service lifecycle. These stages work together to ensure IT services deliver consistent value and align with business objectives. Understanding these stages helps enterprise leaders grasp how IT operations can become more strategic and less reactive.
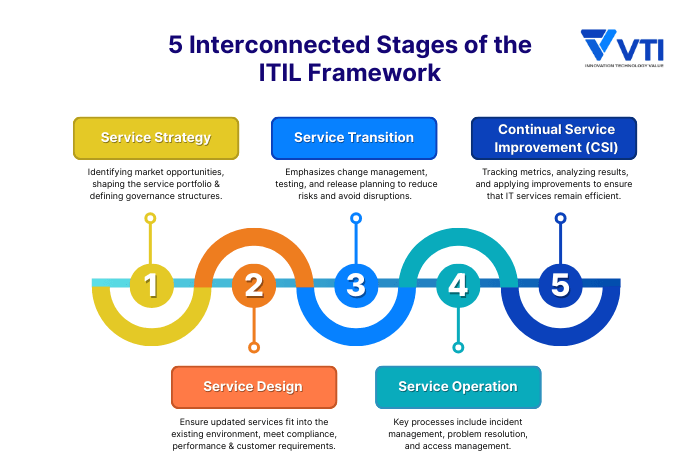
Service Strategy
This is the foundation of ITIL, focusing on how IT services generate business value. It involves identifying market opportunities, shaping the service portfolio, and defining governance structures. For business leaders, service strategy provides clarity on which IT initiatives will deliver the greatest competitive advantage and return on investment.
Service Design
At this stage, strategic objectives are turned into detailed service blueprints. It covers aspects such as architecture, capacity, availability, supplier management, and security. The goal is to ensure new or updated services fit seamlessly into the existing environment and meet compliance, performance, and customer requirements.
Service Transition
Service transition ensures that new or modified services are introduced smoothly into the live environment. It emphasizes change management, testing, and release planning to reduce risks and avoid disruptions. This stage is critical for organizations managing complex infrastructures, as it safeguards operational stability during change.
Service Operation
This is the “business-as-usual” phase where IT services are delivered and supported daily. Key processes include incident management, problem resolution, and access management. Effective service operation directly influences end-user productivity, business continuity, and customer satisfaction.
Continual Service Improvement (CSI)
Rather than a one-time step, CSI is an ongoing cycle of evaluating performance and making enhancements. By tracking metrics, analyzing results, and applying improvements, organizations can ensure their IT services remain efficient, cost-effective, and aligned with evolving business needs.
What Are The Strategic Benefits of ITIL?
Financial Returns and Cost Reduction
ITIL implementation leads to improved cost efficiency by standardizing IT asset and process management, reducing redundant work, and optimizing resource utilization, which lowers operating costs without sacrificing service quality. A global survey found that over half of IT leaders experienced measurable operating cost reductions after adopting ITIL: 26% reported savings up to 10%, and 31% cut costs by as much as 20%.
Calculating precise financial ROI is complex, but dividing ITIL benefits process-by-process (incident, problem, change management) shows tangible avoided costs like downtime, rework, and labor inefficiencies, all contributing to cost reduction.
Service Consistency and Reliability
ITIL enforces standardized IT processes, reducing improvisation and ensuring reliable service delivery without unnecessary delays. Clear processes enable faster responses and incident resolution, minimizing service disruptions and downtime. The University of Oxford reduced major incidents annually from eight to two through ITIL practices.
Tools like failover tests, redundancy, and capacity planning support ITIL in achieving availability and fault tolerance. Proactive incident management with IT visibility and asset lifecycle oversight helps prevent outages and sustain consistent IT performance.
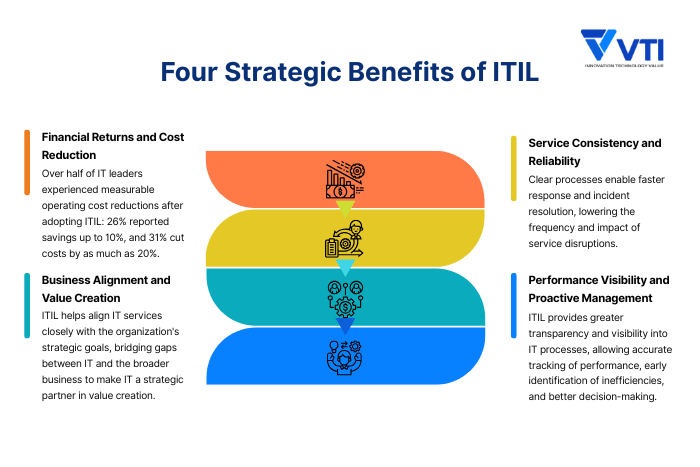
Business Alignment and Value Creation
ITIL helps align IT services closely with the organization’s strategic goals, bridging gaps between IT and the broader business to make IT a strategic partner in value creation.
A case study with a major bank highlighted how improving ITIL processes around infrastructure management bridged disjointed IT-business operations, boosting innovation and competitive advantage. This alignment enables IT to support business objectives effectively, facilitating quicker market response, improved customer experiences, and sustained business growth.
ITIL’s continual service improvement principle ensures IT services evolve with changing business needs and technology trends.
Performance Visibility and Proactive Management
ITIL increases transparency in IT processes, enabling accurate performance tracking and early detection of inefficiencies. Better visibility supports smarter decision-making and enhances incident, problem, and change management. Real-time asset and dependency data enables faster diagnostics and more targeted resolutions.
Asset lifecycle insights, capacity planning, and predictive controls reduce incidents and minimize downtime. These practices shift IT from reactive firefighting to proactive, metrics-driven value delivery.
What Does ITIL Implementation Require?
ITIL implementation demands three critical resources: people, time, and technology infrastructure.
- People and Skills: ITIL adoption requires your sponsorship to build a core team of 2-4 certified professionals ($300-500 per certification), and 6-12 months of organization-wide training.
- Time Investment: Pilot programs for high-impact processes like Incident Management take 3-6 months. Full implementation requires 12-24 months, depending on organizational size and existing process maturity. No shortcuts to build the culture that makes ITIL work.
- Technology: ITSM platforms range from $10,000-100,000+ annually. But buying expensive software doesn’t mean they’re “doing ITIL”. Define your processes first, then select tools, then train the staff.
- Hidden costs include change management, documentation development, and temporary productivity dips during transition.
These barriers explain why many organizations turn to ITIL-certified managed service providers. Instead of building capabilities over two years, you get:
They bring pre-built frameworks, certified expertise, and established ITSM tools from day one. Instead of spending two years building capabilities internally, you gain immediate access to 24/7 monitoring, standardized service desk operations, and proactive IT maintenance, all operating on proven ITIL processes.
For organizations facing the resource constraints outlined above, a faster, more cost-effective path to ITIL maturity, like hiring an outsourcing team, can provide 20-30% operational cost savings within months rather than years.
Hybrid approaches are also an option for concerned clients. For example, outsource operational ITIL processes (Service Operation, Continual Service Improvement) to experienced providers while keeping strategic functions (Service Strategy, Design) in-house.
VTI delivers AI-powered managed services using AuraOps for proactive operations, 30% cost reduction, and 24/7 multilingual support. ITIL-compliant Managed service
How Can Businesses Put ITIL Into Practice?
If you decide to implement the ITIL framework in-house, here are some key recommendations for adopting ITIL effectively:
Strategy and Assessment
First, it’s crucial to define clear business goals and understand ITIL meaning to your organization. This involves securing executive buy-in by demonstrating the value and potential return on investment. Then, you must assess the current IT landscape to identify existing processes, pain points, and opportunities for quick wins, which helps build momentum for the initiative.
Phased Implementation
A successful rollout is planned in manageable phases rather than attempting everything at once. You should prioritize implementing high-impact processes like Incident or Service Request Management first. Throughout this stage, it’s vital to communicate clearly and provide training to ensure teams understand the changes and their roles, which helps overcome resistance and encourages adoption.
Continual Improvement
ITIL is not a one-time project; it is a cycle of continuous improvement fueled by feedback and performance metrics. Businesses should regularly measure key performance indicators (KPIs) to track progress and identify areas for enhancement. As processes mature, the focus shifts to optimizing workflows and automating tasks where possible, embedding a culture of improvement into the organization.
Explore Certification Options
Certification helps validate skills and supports structured adoption. AXELOS, the governing body for ITIL, accredits training providers and certification programs worldwide. Partnering with an Accredited Training Organization (ATO) ensures that the workforce is properly prepared to apply ITIL standards.
Final words
The framework offers enterprise leaders a clear pathway to transform IT from a reactive support function into a strategic business driver. With proven benefits, including a 20-30% reduction in downtime costs and measurable improvements in customer satisfaction. This framework provides the structured approach your organization needs to thrive in today’s digital landscape.
As successful implementations across Asia-Pacific demonstrate, this framework adapts well to diverse business cultures while delivering consistent value. Consider how ITIL’s systematic approach could strengthen your IT operations and business alignment.
FAQ
What is the Difference Between ITIL and ITSM?
The distinction between ITIL and ITSM often creates confusion among enterprise leaders, but understanding their relationship is crucial for making informed technology decisions.
ITSM (IT Service Management) represents the overarching discipline of managing IT services to deliver value to customers and end-users. Think of ITSM as the practice itself – the activities, processes, and organizational approach to managing your entire IT service portfolio.
ITIL, on the other hand, serves as a comprehensive framework of best practices that guides how to implement ITSM effectively. While ITSM defines what needs to be done, the ITIL framework provides specific guidance on how to do it. This distinction becomes particularly important when enterprises evaluate different approaches to service management or consider various ITSM tool implementations.
The ITIL framework offers structured methodologies and proven practices that transform general ITSM concepts into actionable strategies.
For example, while ITSM encompasses incident management as a discipline, the ITIL framework provides detailed guidance on incident categorization, priority matrices, escalation procedures, and performance metrics.
This structured approach helps organizations avoid common pitfalls and accelerate their service management maturity.
What is ITIL Certification?
Earning an ITIL certification demonstrates that an individual has the knowledge and skills needed to apply the framework within an organization. AXELOS, the governing body behind ITIL, provides training and exams through accredited partners. The entry-level credential is the ITIL Foundation Certificate, which is the minimum requirement for anyone who wants to understand, assess, or begin applying ITIL practices.
These certifications are valid for three years and must be renewed through an AXELOS-recognized training provider. On average, each exam costs around USD 300.
Holding an ITIL certification validates your capability to adopt a structured, best-practice approach to IT service management. It signals that you can improve service quality, cut costs, and boost efficiency by following globally accepted standards. Over time, ITIL has evolved through several versions, with each update refining and expanding on the previous one.
With the launch of ITIL 4, AXELOS introduced a new certification pathway to align with modern business and technology needs. The first level, ITIL 4 Foundation, was released in February 2019, followed by higher-level credentials rolled out through 2019 and 2020. The program consists of four tiers:
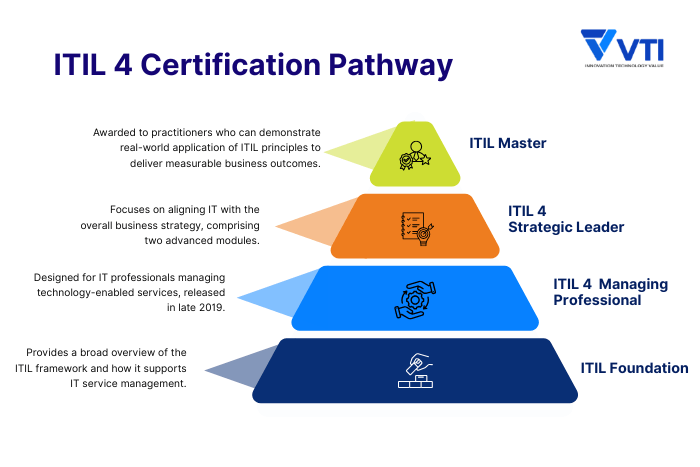
- ITIL Foundation: Provides a broad overview of the ITIL framework and how it supports IT service management. It serves as the entry point for anyone new to ITIL.
- ITIL 4 Managing Professional (MP): Achieved by completing four dedicated modules, this certification path is designed for IT professionals managing technology-enabled services, released in late 2019.
- ITIL 4 Strategic Leader (SL): Introduced in 2020, this track focuses on aligning IT with overall business strategy, comprising two advanced modules.
- ITIL Master: The highest level of ITIL certification, awarded to practitioners who can demonstrate real-world application of ITIL principles to deliver measurable business outcomes.
![[FREE EBOOK] Strategic Vietnam IT Outsourcing: Optimizing Cost and Workforce Efficiency](https://vti.com.vn/wp-content/uploads/2023/08/cover-mockup_ebook-it-outsourcing-20230331111004-ynxdn-1.png)






