For those considering offshore development, you’ve likely heard of the concepts of Agile vs Waterfall development. Furthermore, it’s often said that using Agile development, which is newer than Waterfall development, is better.
However, if Agile development were truly superior, Waterfall would have disappeared from history. In fact, that hasn’t happened.
So, each model has their own place to shine. Let’s explain how Agile vs Waterfall development differ, and which companies or offshore projects they’re suited for.
What is Waterfall Development?
Waterfall development is one of the simplest and earliest methods of software development processes. It’s called “Waterfall” because it directly relates to the sequence of phases.
Each step in Waterfall development flows to the next step like cascading layers of a waterfall.
Phases begin only after the previous phase is completed. The only way to go back to a phase is to start over from Phase 1. In other words, Waterfall is a sequential management process consisting of several discrete phases.
The goal of Waterfall development is to deliver a complete product all at once. This method is mainly suitable for large enterprises and government systems.
However, Waterfall development is considered to be slow to process, difficult to manage, and not very responsive to changes due to the large scope that must be handled.
Waterfall Development Phases
Waterfall development is typically divided into 5-7 phases in strict sequence. The main phases are as follows:
- Requirements
- Design
- Implementation
- Verification
- Maintenance
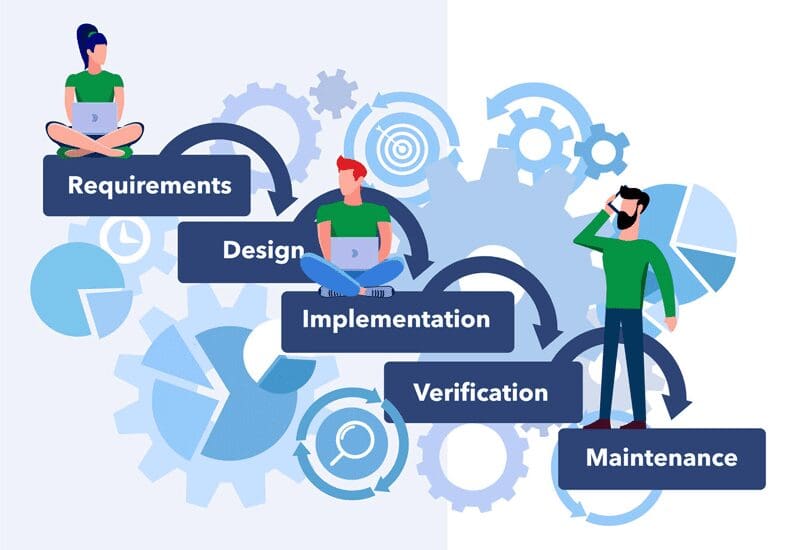
While the specific names of phases vary, they were originally defined by inventor Winston W. Royce as follows:
Requirements:
All requirements are gathered at the start of the project, and all phases can be planned without further contact. Project requirements must be clear to all team members.
Design:
The design phase is typically divided into two sub-phases: logical design and physical design.
Logical design means laying out possible solutions, while physical design means turning those theoretical ideas and schemas into concrete specifications.
No coding is required in this phase, but the team establishes specifications such as programming languages and hardware requirements.
Implementation:
In the implementation phase, coding takes place. Programmers gather information about requirements and specifications from previous phases and create actual code.
They typically implement small code fragments that are integrated at the end of this phase or the beginning of the next phase.
Verification:
In this phase, customers review the product to verify whether it meets requirements.
Testers systematically find and report problems that occur during the testing process. If critical issues arise, the project may need to return to Phase 1 for re-evaluation. Once the product passes this phase, the completed product is released to customers.
Maintenance:
Customers regularly use the completed product during the maintenance phase, discovering bugs, inadequate features, and other errors that occur during use.
When problems arise, the development team needs to create patches and updates to address them. For major issues, the entire process may need to be restarted from Phase 1.
What are the Benefits of Waterfall
Waterfall development is a development method that has been traditionally adopted in many projects. Compared to Agile development, it has the following clear benefits:
- Advantages in Planning and Budget Management. In Waterfall development, it’s possible to clarify the overall project plan and budget in advance. This makes it easier to estimate development costs even in offshore development, allowing for efficient project management.
- Utilization of Expertise and Quality Assurance. The person responsible for each development process has high expertise and can demonstrate technical skills specialized in their assigned process. In Waterfall development, there’s no need to acquire skills outside the process, making it easier to ensure project stability and completeness.
- Clear Division of Responsibilities and Management In Waterfall development, the person responsible and deliverables for each phase are clearly defined, making project management easier. It provides a manageable structure, especially for large-scale projects and compared to Agile offshore development.
- Knowledge Transfer Through Document Emphasis: Detailed documents such as design documents, specifications, and test specifications are created at each stage, enhancing project knowledge transfer and maintainability. This is an important element for long-term system operation.
- Unified Quality Standards: Clear quality standards and verification processes are established for each phase, making it easier to unify the quality of the entire system and meet the strict quality requirements of large enterprises and public institutions.
- Contract Management with Clients Since specifications and deliverables are clarified in advance, the contract scope with clients is clear, and the risk of budget overruns due to additional requirements can be suppressed.
What are the Disadvantages of the Waterfall?
In the Agile Waterfall comparison, Waterfall development has the following challenges:
- High Cost of Rework: In Waterfall development, if problems are discovered at an early stage after project completion, redevelopment requires a lot of time and cost. This point is considered a major disadvantage of Waterfall development in the Agile vs Waterfall comparison.
- Difficulty Responding to Change Requests: Once specifications are decided, changes are difficult, and the system cannot flexibly respond to market changes or changes in customer needs. Especially in rapidly changing fields like the IT industry, this rigidity can lead to decreased competitiveness.
- Long Development Period: Since all processes proceed sequentially, it takes a long time to complete the entire system. In Waterfall development, users can only verify the actual deliverables near the end of the project, risking results different from expectations.
- Risk Concentration in Early Stages: Mistakes in judgment during requirements definition or design stages have a major impact on all subsequent processes. This high initial risk is one of the major differences between Agile vs Waterfall development.
- Lack of Communication Between Teams: Since each phase is independent, continuous communication between development teams tends to be insufficient. This can delay the sharing of requirement interpretation differences or technical problems.
- Delayed User Feedback: Since users can actually use the system only near the end of the project, discovering and correcting usability issues or functional dissatisfaction becomes difficult.
- Delayed Response to Technology Changes: Even if new technologies or tools emerge during the long development period, they are difficult to incorporate into ongoing projects, and the product may be technologically obsolete upon completion.

What to Consider When Choosing “Waterfall” for Offshore Development
After considering product requirements and project scale, if you think Waterfall offshore development is appropriate, pay attention to the following points:
Choose overseas companies with long-term relationships with Japanese companies:
Japanese companies and culture are unique, so without experience cooperating with Japanese companies, communication may not work, customer needs may not be understood, and various problems are likely to occur.
Therefore, companies considering offshore development should prioritize overseas companies that have been active in Japan for a long time.
Provide detailed requirements as much as possible:
A well-known characteristic of the Japanese language is ambiguity, right? However, when consulting with foreigners, if you use Japanese-style speaking, the other party may misunderstand. Especially regarding IT offshore development, rather than saying “that’s not good,” it’s better to point out “what’s not good about it.” In other words, thoroughly avoid ambiguity in conversations with foreigners.
Make reporting efficient and clear:
Clarify from the beginning how often the contractor provides reports and whether the report content is detailed. Also, if there are unclear points in the report during implementation, inquire early.
What is Agile Development?
Agile development is a software development methodology centered on the concept of iterative development, with short operational cycles repeated many times.
Agile development was proposed by a community of developers in 2001. The reason was that they were fed up with the traditional process of “Waterfall” and decided to establish a new manifesto (the Agile Manifesto).
When it comes to Agile, you may hear about Scrum and Kanban models. Since Agile is a way of thinking (or can also be called a methodology), there is no definition of how steps in software development should specifically be considered Agile, but there are only 4 values and 12 principles that actually express the purpose of Agile.
The 4 Values of Agile
- Individuals and interactions over processes and tools: It’s easy to understand that people should be valued more than processes and tools, as it’s people who respond to customer needs and drive the development process.
- Working software over comprehensive documentation: Historically, vast amounts of time have been spent on documentation for product development and final delivery. Agile doesn’t eliminate documentation, but it centralizes and simplifies the documentation necessary for software development.
- Customer collaboration over contract negotiation: The Agile Manifesto describes customers who are involved and cooperate throughout the development process. This makes it much easier to meet customer needs.
- Responding to change over following a plan: Agile’s view is that changes always improve projects or provide added value.
The 12 Principles of Agile
- Improve customer satisfaction through early and continuous software delivery
- Respond to changing requirements throughout the development process
- Deliver working software frequently
- Clients and developers collaborate throughout the project
- Support, trust, and improve motivation for stakeholders
- Enable face-to-face interaction
- Working software is the most important measure of progress
- Support a consistent development pace with Agile processes
- Improve agility through commitment to specifications and design
- Simplicity
- Self-organizing teams promote superior architecture, requirements, and design
- Improve efficiency through regular retrospectives
What are the Benefits of Agile?
Agile development has become the mainstream method in modern software development. In comparison with Waterfall, Agile provides the following significant benefits:
- Rapid Delivery and Market Launch: The Agile development model can provide new products and features to users more quickly. With short sprint cycles, the speed of product launch to market is dramatically improved compared to Agile vs Waterfall development.
- Utilization of Continuous Customer Feedback: Receiving customer feedback while developing software systems benefits both development teams and customers. This continuous improvement process is one of the greatest features of Agile development.
- High Responsiveness to Change Requests: It can respond flexibly and quickly to market changes and changes in customer needs. In comparison to Agile vs Waterfall, this adaptability becomes a major competitive advantage.
- Strengthened Communication Between Teams: Daily standup meetings and retrospectives activate communication within teams, enabling early problem detection and resolution.
- Continuous Quality Improvement: Since working software is provided at the end of each sprint, continuous testing and quality improvement occur, enhancing final product quality.
- Early Risk Detection and Mitigation: Short iterations allow technical problems and business risks to be discovered early and addressed before costs balloon.
- Improved Team Motivation: Autonomous team operations and regular confirmation of results improve development member motivation and productivity.
- Optimized Cost Efficiency: By avoiding the development of unnecessary features and concentrating on truly necessary functions, development cost optimization can be achieved.
What are the Disadvantages of Agile Development?

In the Waterfall vs Agile comparison, Agile development also has the following challenges:
Difficulty Managing Project Direction: Due to flexibility, it’s easy to deviate from the original purpose if not reviewed regularly. This point is one of the major differences between Agile vs Waterfall development.
Budget and Schedule Uncertainty: Continuous changes and improvements can make it difficult to predict final development costs and completion timing. Especially in large-scale projects, this uncertainty becomes a risk factor.
Risk of Insufficient Documentation: Due to emphasizing working software, sufficient documentation may not be created, potentially causing challenges in maintainability and knowledge transfer.
High Skill Requirements: Team members require high communication skills, technical abilities, and autonomy, so securing appropriate personnel can be difficult.
Need for Continuous Customer Involvement: Continuous participation of product owners and customers is necessary, and if securing customer-side resources is difficult, project success becomes challenging.
Management Complexity in Large-Scale Projects: In large-scale projects involving multiple teams, coordination and integration between teams becomes complex, and management challenges may arise.
Ensuring Quality Control Consistency: Since each team develops independently, unifying quality standards and design philosophy across the entire system can become difficult.
Representative Models in Agile
Scrum Model – Is Scrum Agile or Waterfall?
There’s no doubt that Scrum is the most widely used among the many frameworks supporting Agile methodology.
Scrum is an approach that structures software development into short, recurring phases called Sprints.
The purpose of these Sprints is to maximize the efficiency of the development team. Each completed Sprint should contribute directly toward the Product Goal, which is the larger, overall objective of value that the team is trying to achieve with the software.
It’s typically used for software development management, but can be successfully used in business-related contexts.
Each day starts with a small 15-minute meeting. The daily scrum plays a role in synchronizing activities and finding the best way to plan the day’s work, allowing verification of sprint “health” and product progress.
Benefits:
- Team motivation is good because everyone meets the sprint deadlines
- Transparency allows all members within the team and even the entire organization to track the project
- Fewer mistakes because the Scrum model always emphasizes quality
- The dynamics of this model allow developers to reorganize priorities, giving more attention to incomplete sprints
- Proper sprint planning is prioritized so the entire Scrum team can understand the “why, what, and how” of assigned tasks
Drawbacks:
- Due to project subdivision and the pursuit of development agility, teams may lose sight of the entire project and focus on specific parts
- Confusion may arise among team members because they may not clearly define all developer roles
Kanban Model
The word “kanban” comes from Japanese, and its meaning relates to the concept of “just in time.” In practice, the Kanban model is organized on a board or table (Kanban board), divided into columns, showing all flows within a software development project.
As development progresses, the information in the table changes, and each time a new task starts, the team will create a new “card”.
This model is also useful for individual business departments such as HR and marketing, bringing necessary visibility to all team tasks.
The Kanban model requires communication and transparency so that all members can accurately grasp the development stage and status at any time.
It focuses above all on team capacity and is optimal for processes receiving small changes.
Benefits:
- Ability to display all tasks under a single project (e.g., completed, in progress, or under test) using the simple concept of “cards”
- Can limit the number of tasks in progress
- Focuses on cycle duration – the time it takes for a task to move from backlog to the final stage
- Enables continuous delivery
- Perhaps one of the simplest models to implement outside the “IT world”
Drawbacks:
- Team members may misunderstand information on the Kanban board, especially if outdated
- Since Kanban has no timeframe, you may face time-related problems, such as delays at any stage
What to Consider When Choosing “Agile” for Offshore Development
Determine Scope of Work (SoW)
The scope of work is a document containing information about work to be performed in the project. This is the initial agreement that tasks should be completed by the written deadline. The procedure is not intended to show details, but rather the SoW content includes:
- Project milestones and dates
- List of deliverables for each milestone
- Reporting scheme
You should divide each milestone into short parts called iterations. This allows preparation of a rough plan including specific tasks for each iteration, making it easy to prioritize and rearrange those tasks as needed.
Create a Product Roadmap
A product roadmap is a strategic document that serves as a step-by-step guide for the project, consisting of long-term and short-term goals and how to achieve them. This is an overall visual representation of the project that can be transformed over time if requirements, technology stack, or deadlines change.
Creating a roadmap allows a clear representation of the project process. At this stage, the Agile development team can divide each iteration into multiple sprints (standard length is 1 week).
Streamline Communication
In Agile methodology, teams conduct regular short meetings. When managing offshore development teams, these meetings are very important to allow teams to coordinate work with each other.
Below are the three most common types of meetings in offshore development following the Scrum model:
- Daily Standup Meeting: Usually held in the morning, lasting 15-20 minutes. During the meeting, each team member must answer three questions: what did you do yesterday, what will you do today, and what are the current obstacles to performing tasks?
- Planning Meeting to Prepare for the Next Sprint: Sprint goals and sprint backlogs are the outcomes of this meeting.
- Release Planning Meeting Where a Release Plan is Created: The release plan is further used to develop iteration plans.
Not only that, but to achieve communication efficiency, data transparency (between teams and between development teams and customers) should be ensured. Various methods can be utilized, such as centralized data management, using simple words containing only one meaning during consultation, and utilizing tools that support communication and project management.
Adhere to General Agile Standards (such as the 12 Principles)
There are well-known techniques used in Agile software development, such as common coding standards, source control servers, continuous integration, bug tracking, and design patterns. In offshore development teams, these techniques become more important as face-to-face communication decreases.
Make sure you’re using a source code service that allows both onsite and offshore teams to work smoothly. If you’re utilizing a source code management system that can’t handle remote work well, it’s time to look for a different source code management system.
When managing Agile offshore development teams, the need for active collaboration tools (wikis, issue tracking tools, prototyping tools, etc.) also increases.
Thorough Documentation and Sharing
In communication, it’s better to text the conversation content so it remains in form, not just verbally. If disputes or misunderstandings occur, it’s possible to trace them back to the text and grasp the correct intent. Also, when consulting, Japanese companies should speak in Japanese that is as friendly as possible. Simple expressions are more effective in communication than using words known to few people or expressions that are too polite.
Hold Demos Regularly
A demo is a meeting where the team announces the results of their work. Usually, these meetings are held after each sprint, that is, when a specific function becomes usable.
During these meetings, the team receives constructive feedback from the product owner and can adjust their efforts accordingly. Also, the product owner can adjust the workload more effectively, considering the team’s work pace. Because there are so many benefits, please hold demos as regularly as possible.
What are the Differences Between Agile vs Waterfall?
| Comparison Item | Waterfall | Agile |
| Development Approach | Sequential (Requirements → Design → Implementation → Verification → Maintenance) | Iterative/Incremental (repeated short sprints) |
| Planning | Advance overall planning and budget clarification | Adaptive planning, continuous adjustment |
| Change Response | Changes are difficult, high cost | Changes welcomed, flexible response |
| Customer Involvement | Only at the initial requirements definition and final delivery | Continuous cooperation throughout the entire project |
| Delivery Cycle | Batch delivery at project completion | Working software is provided at the end of each sprint |
| Documentation | Emphasizes detailed document creation | Emphasizes working software, minimal necessary documentation |
| Team Structure | Specialized by phase | Self-organizing cross-functional team |
| Quality Control | Unified standards at each phase | Continuous testing and improvement |
| Risk Management | Risks are concentrated in the initial stage | Early detection and mitigation |
| Communication | Limited between phases | Daily standups, active interaction |
| Main Benefits | Clear division of responsibilities Budget management advantage Documents are excellent for knowledge transfer Easy to manage large-scale projects | Rapid market launch Utilize continuous customer feedback Strengthen team communication Optimize cost efficiency |
| Main Disadvantages | High rework costs Long development period Delayed user feedback Delayed response to technology changes | Budget/schedule uncertainty Difficulty managing project direction High skill requirements Risk of insufficient documentation |
| Application Scenarios | Financial/core systems Strictly regulated industries (medical, aviation) Clear requirements, few changes Large-scale complex systems Fixed budget and deadline | Web apps/mobile apps Startups/new businesses Frequent requirement changes Innovation emphasis Small to medium teams |
| Offshore Development Considerations | Select a partner with local coordination experience Provide detailed requirements Efficient and clear reporting system | Determine Scope of Work (SoW) Create product roadmap Hold regular demos Streamline communication |
| Representative Frameworks | Traditional project management | Scrum (sprint-based) Kanban (visual workflow) |
| Success Factors | Stable technology and tools Clear requirements definition Experienced specialists | Adhere to Agile 12 principles Continuous customer involvement Autonomous team operation |
Summary: When to Choose Agile vs Waterfall Development
In modern software development, deciding whether to choose Agile vs Waterfall is a critical judgment. Especially when considering offshore development and Agile, selecting the appropriate development methodology based on the project’s nature and requirements is the key to success.
Situations Where Waterfall Development is Suitable
- Projects with Clear Requirements and Low Change Possibility: Such as financial systems or core business systems, where the risk of specification changes is low.
- Large-scale and Complex System Development: When many stakeholders are involved and strict management is required.
- Highly Regulated Industries: Fields like medical, aerospace, or nuclear, where safety is paramount.
- Fixed Budget / Fixed Deadline Projects: When contractual conditions are strictly defined..
Situations Where Agile Development is Suitable
- Projects with Frequent Requirement Changes: Such as web services and mobile apps that need to respond quickly to market changes.
- Innovation-Focused Projects: Where development involves trial and error with new ideas and technologies.
- Small to Medium-sized Projects: Where easy communication between team members is possible.
- Startups and New Businesses: When market validation and rapid improvement are necessary.
About VTI
VTI provides AI-powered software development, automation implementation, digital transformation, and high-tech services for companies of all sizes across various industries, including retail, manufacturing, construction, finance, transportation, and internet services.
VTI Group has been certified as an AWS Partner, Microsoft Partner, and official partner for Magento, Odoo, ServiceNow, and Salesforce. We have also obtained ISO 27001/2022 security standards, Privacy Mark (P Mark), and international certification CMMI Level 3.
We provide IT services as a partner to hundreds of global enterprises in Asia.
Furthermore, over 1,800 employees working at 8 subsidiaries across these 4 countries fully commit to the success of our clients’ DX revolution.
For questions, consultations, and document requests, please feel free to contact us.
![[FREE EBOOK] Strategic Vietnam IT Outsourcing: Optimizing Cost and Workforce Efficiency](https://vti.com.vn/wp-content/uploads/2023/08/cover-mockup_ebook-it-outsourcing-20230331111004-ynxdn-1.png)





