By 2026, global retail advertising revenue will exceed $1 trillion, with Asia-Pacific markets driving this transformation through AI automation and hyper-personalized commerce (PwC). From Japan’s tech-savvy retailers to Southeast Asia’s marketplaces, the opportunity for any player to define the retail future is wide open.
Will your business lead the $1 trillion transformation, or become its casualty?
Technology disruption is reshaping every touchpoint. AI assistants replace traditional service, generative design accelerates product cycles, and voice commerce eliminates friction. These innovations are setting new expectations across the region’s diverse markets.
In addition, consumer behavior has fundamentally shifted. Brand loyalty is eroding while even affluent customers now prioritize value over prestige (McKinsey). With acquisition costs rising, retail margins across Asia are under pressure.
Despite these challenges, leading companies are already capitalizing on change. Retailers, like Rakuten, Shopee, leveraging AI-driven systems are achieving 25–30% conversion lifts, proving that strategic transformation delivers measurable results.
Success no longer depends on how fast you react. It depends on how far ahead you can see. Retailers who master this transition will define Asia’s retail future through 2030.
Inside This Report
We explore the four forces reshaping Asia’s retail future:
- AI-led Disruption: From product creation to price negotiation, predictive commerce is replacing reactive retail.
- Shifting Consumer Behavior: Meet the “ambient shopper”, always-on, mobile-first, and increasingly loyalty-agnostic.
- Emerging Norms: Retail media and social commerce are no longer optional. They’re essential in Japan, SEA, and Korea.
- Operational Pressures: From labor gaps to fragmented tech, AI-powered agility is no longer a luxury—it’s survival.
You’ll also discover:
- 2026 retail playbook: Four actionable strategies for leaders navigating tech transformation, talent disruption, and shifting demand.
- Key APAC market case studies—from Japan’s retail media boom to SEA’s AI-POS integration
- How to unify platforms, overcome talent gaps, and build data transparency into personalization
Especially: Each section includes a visual infographic distilling the key insights for fast decision-making.
If you’re a retailer in Asia, this is more than a trend report—it’s your strategic briefing for survival and success. The one who act now will shape the next era of commerce in Asia.
1. The Next Tech Leap: From Personalization to Prediction
The retail landscape is entering an era of intelligent automation, where AI is no longer a tool for optimization but the engine of operations. Between 2025 and 2026, market leaders will distinguish themselves not through personalized recommendations alone but through AI-driven business decisions, product innovation, and operational excellence. This transformation marks a fundamental shift in how retailers operate and compete in the modern marketplace.
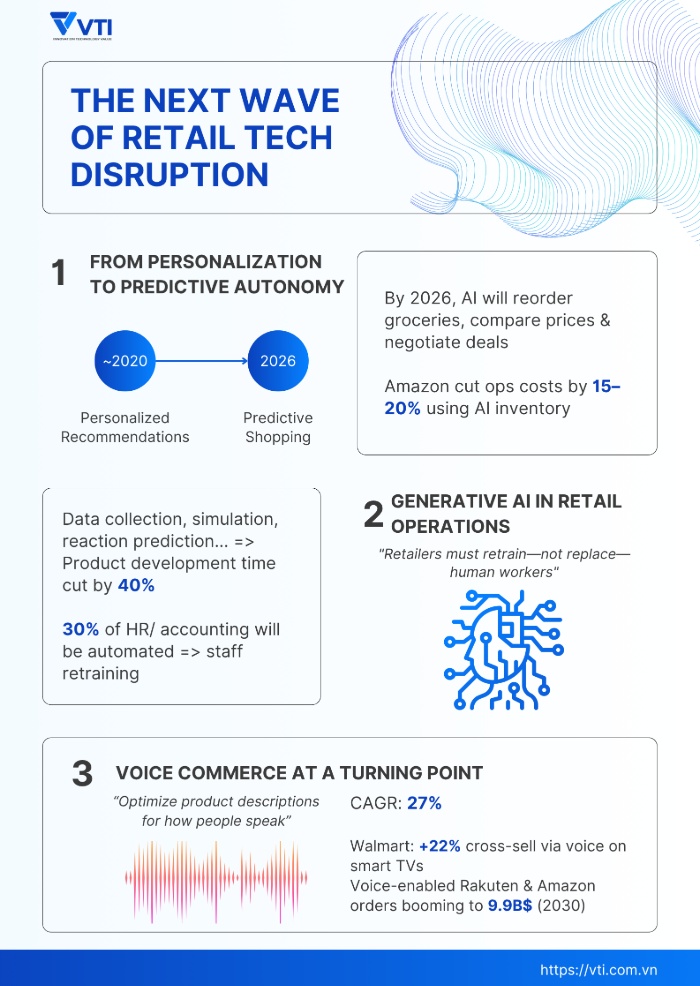
Predictive Autonomy: Beyond Customer Preferences
AI technology in retail is evolving from product suggestions to autonomous purchasing and decision systems. According to Salesforce, by 2026, AI shopping assistants will manage routine transactions (including grocery reordering, cross-platform price comparison, personalized promotions, and loyalty-based incentives) based on customer preferences and real-time inventory data. These systems draw insights from fitness trackers, smart home devices, and purchase history to anticipate needs and automate execution.
Amazon exemplifies this retail digitalization through AI systems that dynamically adjust pricing and inventory based on demand patterns, achieving 15–20% operational cost reductions in select categories (McKinsey, 2025). This shift reflects a broader industry evolution from reactive personalization to predictive commerce models.
Across Asia, retailers are implementing predictive AI tools like AI POS systems to analyze shopper data, which enables demand forecasting before manufacturing begins, reducing inventory waste and the need for markdowns.
Generative AI: Transforming Operations Beyond Content
Generative AI’s impact extends beyond content creation into core operations and product development. For example, AI-powered systems now streamline the product development process by providing a powerful tool that can simulate customers’ reactions and generate virtual product concepts. Being able to virtually test product ideas and prototypes helps cut product development timelines by up to 40%, reducing time-to-market (RTS Labs, 2025).
Korean e-commerce platforms have implemented generative AI for automated product description creation and localized marketing content, streamlining operations across multiple regional markets while maintaining cultural relevance.
Workforce Evolution: The Human-AI Partnership
This operational revolution brings a parallel need for workforce transformation. Generative AI is expected to automate up to 30% of HR, accounting, and compliance tasks by 2026 (Workhuman, 2025). To remain competitive, retailers must implement strategic retraining programs, helping employees become aware that they are not replaced by AI, but rather as supervisors, analysts, and interpreters of AI systems.
Success requires reskilling both frontline and office personnel to manage AI tools, analyze performance, and make informed decisions that guide technology rather than follow it.
Voice Commerce Reaches Its Inflection Point
Voice commerce (shopping through smart speakers, voice assistants, and connected cars) is expected to grow at a 27% compound annual growth rate through 2026 (Business Dasher, 2025). In Asian countries like Japan, this has been integrated into major e-commerce platforms like Rakuten and Amazon Japan, facilitating voice-enabled orders, reorders, and reservations.
This market was valued at approximately $2.47 billion in 2024 and is forecasted to grow to nearly $9.9 billion by 2030 (Grand View Research). Therefore, retailers must now optimize product metadata and descriptions for natural language queries and voice-activated search to remain relevant in this space.
Globally, companies like Walmart have already seen a 22% increase in cross-selling through voice integrations in their smart TV platforms (Marketing Brew, 2025). In other words, voice commerce is more than a novel interface; it is becoming a core driver of omnichannel growth.
Strategic Takeaway
The convergence of predictive AI, operational automation, and voice-driven commerce is not just reshaping retail future. It is redefining what competitive advantage means. Success in this new landscape will depend on bold investment in AI infrastructure, workforce transformation, and leadership that embraces autonomy over automation.
2. Predicting 2025–2026 Consumer Behavior
As the retail landscape rapidly evolves, the psychology of modern shoppers is also changing in fundamental ways. The retail future will require businesses to serve consumers who are more connected, skeptical, and convenience-driven than ever before. These behavioral shifts reflect structural changes in how consumers engage with retailers, accelerated by technology, economic uncertainty, and generational turnover across Asia-Pacific.

The Rise of the Ambient Shopper
One of the most significant changes in the future of retail shopping is the emergence of the “ambient shopper”, who shops passively and continuously while doing other activities. According to NielsenIQ, nearly 70% of consumers engage in “continuous commerce” (ongoing shopping behavior), making purchases while streaming videos on Netflix, Prime, Disney+, browsing social media, or traveling to work. This shift toward always-on commerce creates demand for seamless, contextual shopping experiences across multiple platforms.
This shift has not gone unnoticed by retailers. Retail media networks (advertising platforms within shopping websites and apps, owned by retailers) have capitalized on this behavior to drive retail digitalization. For example, Amazon’s advertising revenue reached $56.2 billion in 2024, thanks partly to shoppable ads embedded within streaming platforms and gaming environments. As consumer attention becomes more fragmented, commerce must follow customers into content, social feeds, and everyday moments.
Quick Commerce as Standard Expectation
Speed is no longer a luxury feature but has become a basic expectation. A recent McKinsey study found that 78% of global consumers are willing to pay extra for two-hour delivery, particularly in urban markets where convenience is highly valued.
In Asia, this demand has led to the expansion of dark stores (small warehouses designed for online orders) and micro-fulfillment centers that reduce delivery times to under 90 minutes. However, quick commerce presents challenges for future stores seeking profitability. Despite rising demand, net profit margins remain low, typically just 3–5%, due to high fulfillment costs.
In response, retailers are looking for AI-based demand forecasting, route optimization, and hybrid delivery systems that blend human couriers and autonomous vehicles.
These investments are no longer optional—they have become core brand differentiators in an omnichannel economy.
Building Trust Through Radical Transparency
Trust remains a fragile but essential element in the digital economy that influences the future of shopping. As consumers grow more privacy-aware and data regulations tighten, brands that fail to offer transparency risk losing customers permanently. NielsenIQ reports that 58% of consumers have switched brands due to unclear data policies or weak loyalty offerings. Accordingly, by 2026, trust is projected to depend on visible ethical commitments and transparent business practices.
Retailers like Kroger are already using blockchain-enabled supply chains to provide real-time tracking. Not only help reduce supplier audit costs by 35%, but it also boosts consumer trust.
Mobile-First Expectations and Payment Flexibility
Today’s consumers expect not just speed but seamless experiences, especially on mobile devices. In APAC regions, over 80% of e-commerce traffic now originates from smartphones, according to Statista. This mobile-first behavior shapes not only UX design but also checkout processes, with rising demand for tap-to-pay, biometric login (fingerprints or face recognition), and native in-app checkout systems.
Payment expectations have also become critical in the modern retail landscape. Features such as Buy Now, Pay Later (BNPL), digital wallets like LINE Pay and KakaoPay, and cross-platform loyalty integrations are no longer nice-to-have features but must-have requirements for successful sales conversion. Retailers who fail to offer these flexible payment options risk losing customers at the moment of checkout, especially among younger consumers in Gen Z and Gen Alpha.
Experiential Retail 2.0
As digital commerce grows, physical retail is being reinvented rather than eliminated. Across Asia, future stores are seen to become hybrid environments combining instant fulfillment with community-based experiences, which reflects a deeper insight into the desire for both convenience and human connection. This also represents a retail future blurring traditional boundaries between online and offline shopping.
For example, in South Korea, department stores are converting space into art installations, wellness zones, and product trial lounges, driving foot traffic and increasing the time customers spend in stores. Similarly, Japan’s retail hubs are focusing on experiences such as unmanned stores, robot-led shopping assistance, and AI-curated pop-up events.
Savills forecasts that experiential retail formats will account for 25% of APAC retail leases by 2026, particularly in major cities where foot traffic is high but attention spans are short. These environments blur the lines between commerce, entertainment, and community, fundamentally reshaping the physical footprint of the retail future and setting new standards for retail store trends across the region.
Strategic Takeaway
These interconnected behavioral shifts signal a permanent evolution in consumer psychology. Retailers who recognize these changes as complementary forces rather than isolated phenomena will be best positioned to thrive. Success in 2025-2026 will require integrated strategies that seamlessly connect speed, transparency, mobile optimization, and physical experiences into cohesive brand ecosystems that meet consumers wherever and however they choose to engage.
3. Market trends reaching maturity
While disruptive technologies like AI dominate headlines, the retail future in 2026 will also be defined by trends that have matured into new industry standards. These are now deeply embedded in the retail landscape, reshaping how businesses should generate revenue, engage customers, and design their supply chains.

The Trillion-Dollar Retail Media Ecosystem
Retail media networks (RMNs) have transformed from a side “hustle” to a core profit engine. According to Grand View Research, global advertising spending on RMNs is projected to reach $1.23 trillion by 2026, capturing over 55% growth between 2024 and 2028. This massive rise demonstrates how retail digitalization is creating new revenue opportunities beyond traditional product sales.
While Amazon remains the dominant force in this space, competition is intensifying across the retail industry. Walmart Connect reported $4.4 billion in revenue in 2024, fueled by off-site targeting (advertising beyond their website) and connected TV integrations (advertising on streaming platforms).
In Asia, regional players such as Shopee Ads and Rakuten Marketing are also leveraging first-party purchase data about what customers buy to drive campaign performance and closed-loop attribution (tracking advertising results from start to purchase).
Beyond generating revenue, RMNs deliver profit margins as high as 60–70%, far exceeding traditional retail categories like grocery or clothing, according to McKinsey. For business financial leaders, this transforms advertising from a marketing expense into a high-margin revenue stream, creating incentives to invest in media infrastructure and specialized talent.
Social Commerce as Retail Future’s Default
In parallel, social commerce (buying products through social media platforms) used to be seen as a trend for younger consumers, but is now a mainstream retail engine transforming omnichannel retailing strategies.
In Southeast Asia, livestream shopping revenues surged 210% year-over-year in 2024, while TikTok Shop commands 18% of Indonesia’s e-commerce market. Globally, in-app checkout, influencer storefronts, and video-first product discovery are driving measurable increases in sales conversion rates.
Retailers have shifted their approach from traditional influencer marketing to conversion-centric content strategies, focusing on actual sales rather than just brand awareness. For example, educational livestreams, interactive product demonstrations, and AI-personalized recommendations outperform passive advertising campaigns, particularly when paired with time-bound offers or gamified engagement.
This transformation is also challenging existing attribution frameworks (methods for tracking which marketing efforts lead to sales). In response, brands are adopting multi-touch tracking models that capture customer behavior across discovery, engagement, and conversion phases, redrawing the customer journey funnel in the modern retail landscape. This shows how future shops must adapt their measurement and analytics to understand the complex path customers take from social media impressions to final purchases.
Sustainability as Standard, not Strategy
By 2026, sustainability will no longer be a brand differentiator but will become a standard. According to WGSN and Springfair, 83% of consumers expect brands to show measurable commitments to ethical sourcing, recyclable packaging, or environmental transparency. This shift represents a fundamental change in retail industry growth priorities, where corporate responsibility becomes as important as product quality and price.
Leading private-label retailers such as H&M are responding with circular models (promoting reuse, repair, and resale rather than disposal). Their resale platform saw 140% growth in 2024, driven by AI-based style matching and personalized alerts for pre-owned inventory. This demonstrates how retail digitalization can support the challenge of balancing sustainability and profitability.
This reflects deeper psychological changes in consumer behavior. They use those visible sustainability practices as indicators of trustworthiness and quality when choosing brands. Retailers are adapting by integrating carbon scores, traceability labels, and eco-indexes directly into product pages, blending regulatory compliance, transparency, and marketing value into a unified customer experience.
Strategic Takeaway
As these trends mature into structural expectations, media monetization, social conversion, and ethical commerce, retailers must stop treating them as experiments. In the retail future, success will come from standardizing these capabilities, integrating them into core P&L, operating models, and customer journeys.
4. Economic Outlook & Impact on Retail Future
While digital innovation and evolving consumer behaviors dominate headlines, macroeconomic realities will exert equal, if not greater, pressure on retail strategies through 2026. Slower economic growth, persistent inflation, and shifting regional dynamics are anticipated to affect business decisions.
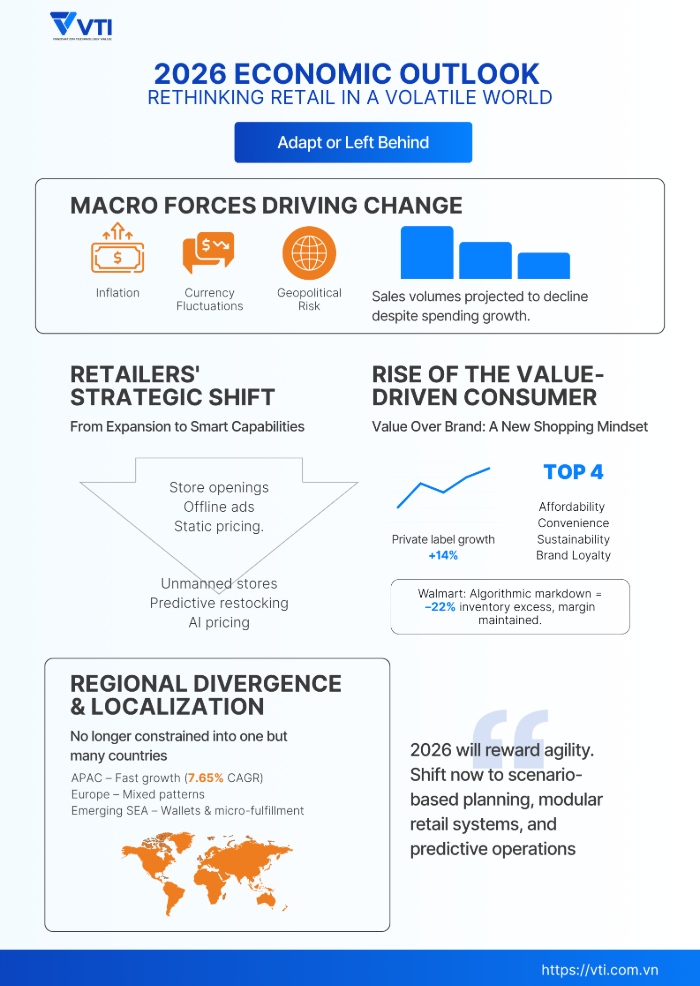
Navigating Global Growth Deceleration
According to the World Bank’s Global Economic Prospects, global GDP growth is projected to slow to 2.9% in 2025–2026, driven by geopolitical tensions, policy tightening, and ongoing supply chain vulnerabilities. Retailers in mature markets such as the United States, Europe, and Japan are expected to see retail sales volumes decline by 2.1%–2.5%, despite nominal growth in spending (McKinsey, 2025).
Moreover, inflation remains a major concern, even in Japan, not just in raw materials and labor costs, but in logistics and energy expenses that affect the entire retail future landscape. As a result, operational agility and demand-based cost control will be essential for future stores. To preserve margins, businesses must prioritize localized pricing, flexible sourcing, and AI-based cost optimization.
Currency volatility (rapid changes in exchange rates) is also influencing procurement, especially for retailers sourcing products across international borders. Import-heavy sectors like electronics and fashion are particularly exposed, with delayed shipments and cost pass-through challenges affecting profit margins in the first half of 2025 (Statista, 2025).
In response, many global retailers are reallocating capital away from physical store expansion and toward automated fulfillment, AI-based pricing models, and predictive analytics platforms. Japanese major retailers like Aeon and Don Quijote are implementing AI-powered systems for predictive restocking, frictionless checkout, and real-time shelf analytics; a big convenience chain has opened more than 200 new unmanned stores.
These moves signal a shift from physical growth to capability building, a strategy better suited to an incoming volatile environment.
Value-Driven Consumer Becomes the Norm
This economic shift is also reshaping consumer behavior in permanent ways, influencing the future of retail shopping. Even well-off shoppers are choosing less expensive alternatives, where private-label grocery sales expanded by 14% in 2024 (McKinsey, 2025). This is not just a temporary cost-saving trend but a reflection of a broader reorientation toward a perceived value and disciplined shopping trend.
NielsenIQ reports that 80% of global consumers cite affordability as their top concern, even when buying non-essential items. Retailers are responding with dynamic pricing, AI-driven promotional optimization, and curated value offerings that deliver flexibility without sacrificing profit margins. Walmart, for example, has deployed algorithmic markdowns (computer-controlled price reductions) that reduced excess inventory by 22% while preserving profitability.
At the same time, payment preferences are shifting toward flexible financing. Buy Now, Pay Later (BNPL) adoption continues to grow in Asia and Latin America, especially among Gen Z and Millennial shoppers. According to PwC, retailers integrating frictionless financing into mobile and in-store journeys are seeing higher conversion rates and repeat customer engagement.
Regional Divergence Requires Localized Strategy
While mature economies face economic stagnation, the Asia-Pacific remains a global engine driving retail industry growth. Savills projects retail revenues in the region to grow at a 7.65% compound annual growth rate through 2030, driven by urbanization, digital adoption, and a rising middle class. Countries such as the Philippines, Indonesia, and Bangladesh are seeing an influx of retail innovation, from digital wallets to hyperlocal fulfillment models.
Meanwhile, the retail environment in Europe shows more fragmented patterns. Germany and the Nordic countries are reporting slower foot traffic and investment pullback, while Eastern Europe benefits from local manufacturing and logistics reconfiguration.
This regional divergence demands hyperlocalized strategies that go beyond simple market adaptation. Inventory planning, brand positioning, and go-to-market models must reflect cultural differences, regional economic maturity, and digital infrastructure capabilities.
For multinational retailers, this complexity has created a critical operational challenge: managing disparate systems across markets while maintaining strategic coherence. Most global retailers operate fragmented technology stacks, with separate platforms for each country or region that cannot communicate effectively. This siloed approach prevents real-time visibility into global performance metrics and limits the ability to optimize inventory allocation, pricing strategies, and promotional campaigns across markets.
Adapting to a Volatile Retail Future
The retail landscape will reward adaptability over raw scale, as regional diversity, technological disruption, and shifting consumer behaviors reshape the rules of competition.
In fast-evolving markets like Japan, Vietnam, and Indonesia, legacy growth strategies, built on physical expansion and volume, no longer guarantee success. This is a moment of inflection, where innovation, agility, and strategic foresight become the core drivers of market leadership.
To thrive, retailers must invest in scenario-based forecasting, embrace cost-flexible operating models, and deploy modular systems capable of responding to real-time shocks—whether economic, geopolitical, or consumer-driven.
Businesses across Asia that reallocate capital toward agility, predictive analytics, and localized responsiveness will gain a decisive edge over competitors still anchored to outdated, one-size-fits-all strategies.
5. The Barriers to Retail Future: What Must Be Solved by 2026
Even though leading retailers talk about embracing AI, social commerce, and automation, many are still held back by outdated systems, scattered data, and disconnected business processes. Without addressing these internal bottlenecks, strategic ambitions for the retail future – whether hyper-personalization, quick commerce, or omnichannel retailing – risk stalling completely. Solving these problems is no longer optional for success but has become the threshold for the modern retail landscape.
Department-Level Friction Points
Marketing: Fragmented Data, Weak Personalization
Retail marketers struggle with fragmented customer data across channels, preventing effective personalization and omnichannel campaigns. NielsenIQ found that 58% of consumers switched brands due to poor membership programs. Retailers like Carrefour are closing this gap by implementing Customer Data Platforms (CDPs) that unify data sources and boost campaign ROI through improved targeting and engagement.
Sales: Incompatible Systems, Frustrated Shoppers
Many chains can’t sync online and offline sales systems, making dynamic pricing and forecasting impossible. One Southeast Asian department store’s conflicting mobile/in-store promotions caused inventory depletion and 12% more customer complaints. Real-time integration across POS, e-commerce, and inventory systems is essential.
Store Operations: Labor Mismatch Hurts CX
Poor workshift management remains a major issue despite technological advances. Orquesta identifies misaligned staffing with foot traffic as a top revenue loss driver. Retailers need traffic-aware work shift scheduling and mobile tasking to optimize labor costs and service levels.
Logistics: Speed Expectations vs. Fulfillment Reality
Quick commerce demands exceed static restocking capabilities. Multi-node networks (distribution systems with multiple locations) require predictive restocking, real-time warehouse orchestration (coordinating multiple warehouse operations), and supplier scorecards.
ESG-compliant supply chains are becoming mandatory to avoid reputational and regulatory risks.
Customer Service: AI Without Integration = Friction
Consumers expect 24/7 multilingual support, but disconnected ticketing systems fragment experiences. Although AI chatbots are becoming more common in future shops, they often lack integration with live support or real-time product data, breaking the service loop.
HR & Finance: Legacy Systems Block Strategic Agility
Retail’s front-line labor model is being disrupted by automation, while finance departments face pressure to deliver faster, more granular reporting for better business decisions. Yet many teams still operate on legacy ERP systems, not designed for predictive insights. McKinsey (2025) shows retailers with real-time finance dashboards achieve 22% better cash flow accuracy, demonstrating the competitive advantage of modernized financial systems.
Cross-Platform, Technical Gaps
But these department-level roadblocks are only part of the picture. At a structural level, many retailers are still struggling to integrate core technologies, hindering transformation at scale.
System Integration
POS, CRM, ERP, and e-commerce platforms operate in silos, especially when bridging legacy systems like AS/400 (older mainframe computer systems). This integration complexity constrains innovation and prevents agility in campaign deployment and inventory rebalancing, limiting omnichannel effectiveness.
Data and AI Infrastructure
Despite retail big data analytics being projected to reach $14.1 billion by 2026 (KBV Research), many organizations lack centralized data lakes or real-time pipelines. Without clean 360° customer views, AI applications for demand forecasting, churn modeling, and cross-selling underperform.
Cybersecurity and Compliance
Digital touchpoint proliferation expands threat surfaces (potential security vulnerabilities) for future stores. New privacy laws across the EU, U.S., and Asia require comprehensive data management and encryption; however, many rely on outdated access controls and fragmented compliance processes, risking breaches and penalties.
Process Automation
While robotic process automation (RPA) rises, use cases remain isolated from broader business systems. Without integration into AI decision engines or real-time business rules, RPA may inefficiently automate rather than eliminate the problem.
Customer Experience Platforms
Customers expect personalized journeys across email, mobile apps, stores, and social media. Fragmented technology stacks create broken handoffs—like mobile promotions unrecognized by in-store staff—causing frustration and missed sales opportunities.
The Retail Execution Gap
As retailers shift from experimentation to enterprise-wide deployment, technology alone is no longer the bottleneck—execution is. High-performing organizations are not defined by how many tools they adopt, but by how well they embed those tools across functions with clear ownership, consistent governance, and cross-functional alignment.
Academic frameworks such as the Digital Maturity Index and McKinsey’s Digital Quotient suggest that high performers distinguish themselves not by adopting new tools, but by embedding them across business functions with discipline and cross-team collaboration.
For Asia’s retail players, to lead the $1 trillion transformation, it is about building not only the infrastructure but the internal cohesion.
6. Playbook for 2026: Proactive Strategies for Future Success
Competing in the 2026 retail environment requires more than adopting new tools. It demands reengineering how technology, data, and human capital work together across the business. This playbook outlines four must-execute strategies that pioneering retailers must begin implementing by mid-2025 to lead in tomorrow’s AI-powered, experience-driven market.
Architect AI Agent Ecosystems
AI agents will handle nearly half of all online shopping tasks by 2026, according to Salesforce projections. These digital assistants will search for deals, manage subscriptions, and place orders for customers without human help.
To succeed in this new retail trend, stores must organize their product information so these AI systems can easily find and understand it.
For example, Home Depot improved its product data with detailed tags and descriptions, which helped AI systems find its products 31% more often. Meanwhile, several mid-sized U.S. stores that ignored this trend saw their online product visibility drop significantly in 2024.
Invest in Logistics as a Brand Asset
Fast, reliable delivery has become as important as product quality in today’s retail industry growth. McKinsey’s research shows 78% of customers worldwide will pay extra for a two-hour delivery service. Smart retailers now view delivery and warehousing as ways to build customer loyalty, not just business costs.
This means building small warehouses in cities, using AI to predict where products should be stored, and testing self-driving delivery vehicles.
Kroger’s partnership with Nuro (a self-driving delivery service) achieved 98% on-time delivery for fresh foods and reduced waste by 17%. Retailers without flexible delivery options saw their profit margins shrink in 2024, especially in the grocery, beauty, and fashion categories.
Monetize First-Party Data Through Retail Media
Retail media networks is expected to generate $1.23 trillion globally by 2026. Therefore, it is time that Asian retailers considered whether to build their advertising platform or depend on others for revenue.
Success requires creating systems that track customer behavior from advertisement to purchase, offering AI-powered customer groups to advertisers, and designing custom ad formats for TV and mobile apps.
Such as Target’s Roundel network shows strong results with 45% of sales increases in some product categories coming from their retail media advertising.
Future-Proof the Workforce
While technology advances rapidly, human employees remain the bridge between data, systems, and customer satisfaction. Research indicates 60% of retailers plan to retrain staff by 2026, focusing on AI oversight, data analysis, and omnichannel retailing.
Retailers must shift from basic training to skill-building programs that include online learning platforms, practical scenario coaching, and opportunities to work across different departments.
Looking at global practices, Best Buy’s Techtonic program trained over 12,000 employees in digital skills, reducing employee turnover by 29% and speeding up their omnichannel rollout. Companies that haven’t started similar programs now face higher employee turnover and growing gaps in digital skills.
Conclusion: The Ideal Retailer of 2026
The retail future leaders won’t be defined by size or legacy, but by their foresight, adaptability, and precision in execution. As this report has shown, success in the next era hinges on mastering a new equation: AI-driven intelligence + seamless operations + human adaptability.
Retail is no longer a business of waiting for demand. It’s about anticipating it, through predictive systems, voice-driven commerce, and real-time visibility into every customer journey. Also about orchestrating fast, resilient logistics as a brand asset, and turning customer data into revenue and frontline employees into AI collaborators.
Those who act now, before these shifts become standard, will define the retail future of next decade across Asia.
The playbook is clear:
- AI-Agent Ecosystems – Build systems enabling automated purchasing by AI agents.
- Logistics as Brand Asset – Use fast, reliable delivery to build customer loyalty, not just manage costs.
- Retail Media Networks – Generate additional revenue while gaining deeper customer insights.
- Future-Proof Workforce – Train employees on AI, develop hybrid skill sets, and create flexible roles.
To turn these insights into real business results, retailers should start transforming now. But transformation demands more than intention; it requires a 12–18-month transformation roadmap and a partner that comprehend the retail industry landscape.
Your Transformation Partner in Asia
VTI offers end-to-end digital transformation solutions tailored to the discussed realities of Asia’s dynamic retail markets. From system integration and data infrastructure to AI implementation and workforce development. We help retailers build the technological foundation needed to thrive in the competitive landscape.
Our experience delivering results for major retailers across Japan, Korea, and the APAC region gives us a deep understanding of diverse retail markets and cultural nuances as well as the insight to move fast, mitigate risk, and drive sustainable results. Most importantly, the multilingual team (Japanese, Korean, English) enables seamless collaboration and ensures clear communication throughout complex transformation projects.
By partnering with VTI, retailers can own a customized digital transformation journey while leveraging proven expertise from successful implementations across Asia’s most demanding markets.
Lead the retail future – don’t chase it. Contact us right now!
![[FREE EBOOK] Strategic Vietnam IT Outsourcing: Optimizing Cost and Workforce Efficiency](https://vti.com.vn/wp-content/uploads/2023/08/cover-mockup_ebook-it-outsourcing-20230331111004-ynxdn-1.png)





